Explain the Typical Shapes of the Marginal-benefit and Marginal-cost Curves.
How are these curves used to determine the optimal allocation of resources to a particular product. It is due to the law of diminishing marginal utility.
Solved Specify And Explain The Typical Shapes Of Marginal Benefit Chegg Com
It is due to the law of diminishing marginal utility.

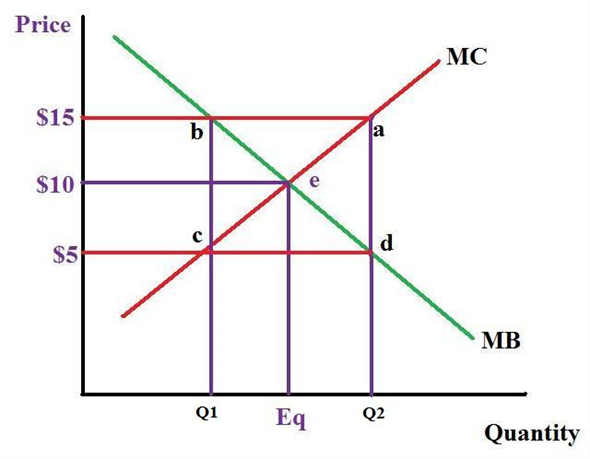
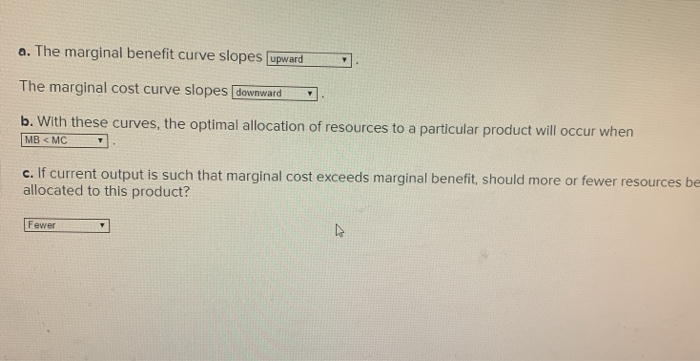
. The marginal-benefit curve will slope downward as the total benefit from one additional unit of an activity increases while the marginal-cost curve will slope upward as the total cost from one additional unit of an activity increases. If current output is such that marginal cost exceeds marginal benefit should more or fewer resources be allocated to this product. See answer 1 Best Answer.
KEY QUESTION Specify and explain the typical shapes of marginal-benefit and marginal-cost curves. How are these curves used to determine the optimal allocation of resources to a particular product If current output is such that marginal cost exceeds marginal benefit should more or fewer resources be allocated to this product Explain. If current output is such that marginal cost exceeds marginal benefit should more or fewer resources be allocated.
Specify and explain the typical shapes of marginal-benefit and marginal-cost curves. If current output is such that marginal cost exceeds marginal benefit should more or fewer resources be allocated to this product. B How are these curves used to determine the optimal allocation of resources to a particular product.
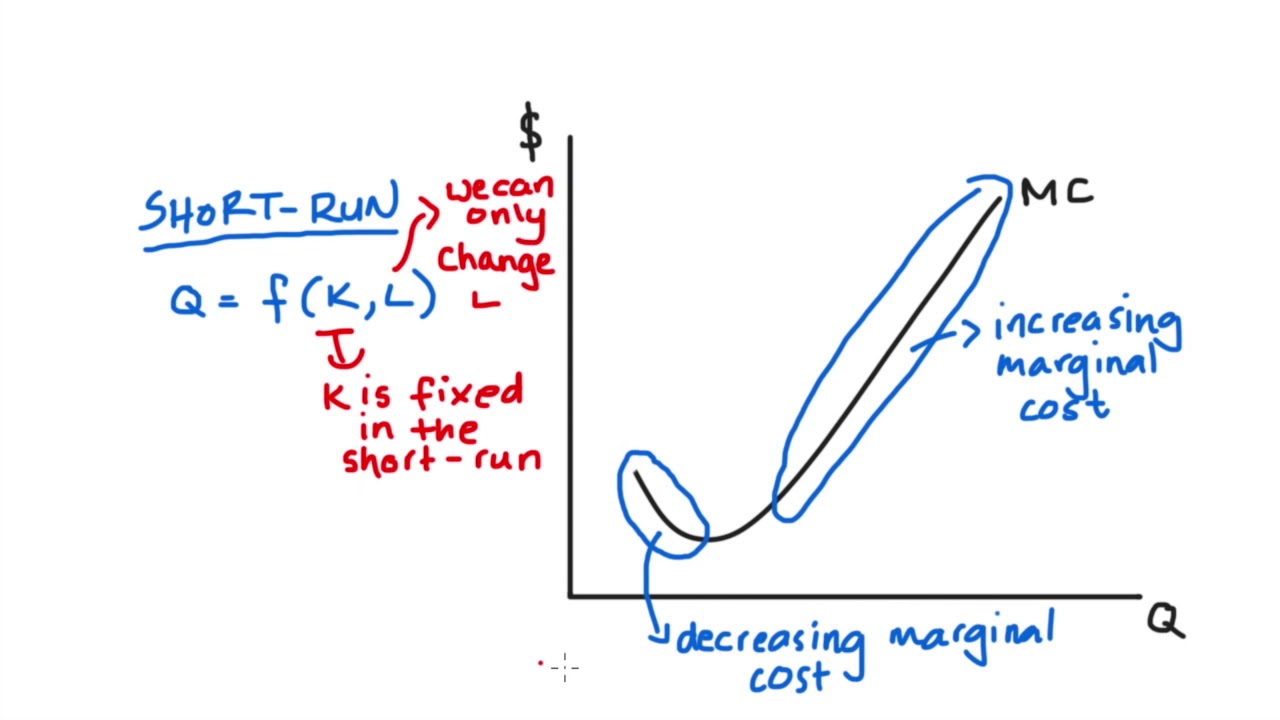
Explain in details with an. How are these curves used to determine the optimal allocation of resources to a particular product. Marginal cost curve is upward sloping because of the law of increasing opportunity cost.
1 Answer to Specify and explain the typical shapes of marginal-benefit and marginal-cost curves. Specify and explain the typical shapes of marginal-benefit and marginal-cost curves. Specify and explain the typical shapes of marginal-benefit and marginal-cost curves.
A Specify and explain the typical shapes of marginal-benefit and marginal-cost curves. How are these curves used to determine the optimal allocation of resources to a particular product. Specify the typical shapes of marginal-benefit and marginal-cost curves.
Specify and explain the typical shapes of marginal-benefit and marginal-cost curves. - The marginal benefit curve is downward Correct sloping. Specify and explain the typical shapes of the marginal-benefit and marginal-cost curves.
Marginal cost curve is upward sloping because of the law of increasing opportunity cost. If current output is such that marginal cost exceeds marginal benefit should more or few resources be allocated to this product. The marginal-benefit curve is downward sloping.
Unlike the marginal cost curve whose slope is often upwards the. How are these curves used to determine the optimal allocation of resources to a particular product. Explain the typical shapes of the marginal-benefit and marginal-cost curves.
The marginal benefit curve is downward. The marginal cost curve is upward. Marginal Benefit curve is usually downward sloping whileMarginal Cost is usually upward sloping.
The marginal cost curve is upward sloping MC increases as more of a product is produced since additional units require the use of increasingly unsuitable resource. With these curves the optimal allocation of resources to a particular product will occur when. Marginal benefit curve is a downward sloping curve because the addition to the total benefits decreases from the consumption of each successive unit of the good.
The marginal cost curve is upward sloping MC increases as more of a product is produced since additional units require the use of increasingly unsuitable resource. How are these curves used to determine the optimal allocation of resources to a particular product. The marginal benefit curve is downward sloping MB falls as more of a product is consumed because additional units of a good bring less satisfaction than previous units.
If current output is such that marginal cost exceeds marginal benefit should more or fewer resources be allocated to this product. Marginal benefit and marginal cost are two measures of how the cost or value of a product changes. If current output is such that marginal cost exceeds marginal benefit should more or fewer resources be allocated to this product.
A The marginal benefit curve is downward sloping MB falls as more of a product is consumed because additional units of a good yield less satisfaction than previous units. When the marginal-benefit and marginal-cost curves intersect or when marginal benefit is as great as marginal cost that is the point where it. - The marginal cost curve is upward Correct sloping.
Marginal benefit curve is a downward sloping curve because the addition to the total benefits decreases from the consumption of each successive unit of the good. How are they used to determine the optimal best output mix in a production possibilities curve. Marginal benefit impacts the customer while marginal cost impacts the producer.
How are these curves used to determine the optimal allocation of resources to a particular product. The marginal-cost curve is upward sloping. Specify and explain the typical shapes of marginal-benefit and marginal-cost-curves.
This video is the second video in a series covering the topic of Market Failure for the IB International Baccalaureate Diploma Programme.
Solved File Edit Viewhistory Help E 30 Thu 9 09 Pm A Chegg Com
The Shape Of The Marginal Cost Curve Youtube
Solved A The Marginal Benefit Curve Slopes Upward The Chegg Com
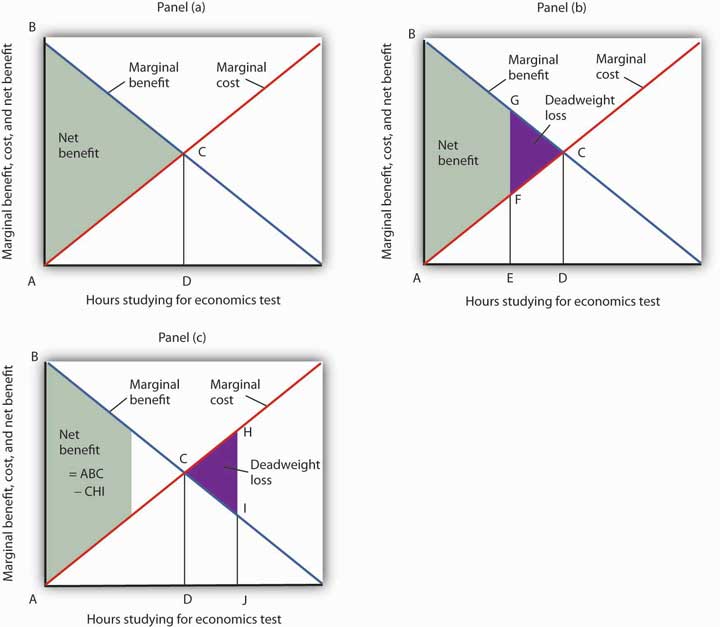
6 1 The Logic Of Maximizing Behavior Principles Of Economics

Cost Notes Lecture All Cost Curves Numerical Examples Theory Notes

The Shape Of The Marginal Cost Curve Youtube

The Graph Shows The Marginal Cost Curve Average Total Cost Curve Demand Curve And Marginal Revenue Study Com

Cost Notes Lecture All Cost Curves Numerical Examples Theory Notes
0 Response to "Explain the Typical Shapes of the Marginal-benefit and Marginal-cost Curves."
Post a Comment